Gross Building Area Uncovered: A Key Metric in Real Estate
Gross Building Area (GBA) is a measurement standard for multi-family buildings and commercial properties. This guide explores the definition of GBA, how to measure GBA by hand or using modern software tools like RoomSketcher, and how GBA compares to other measurement standards.
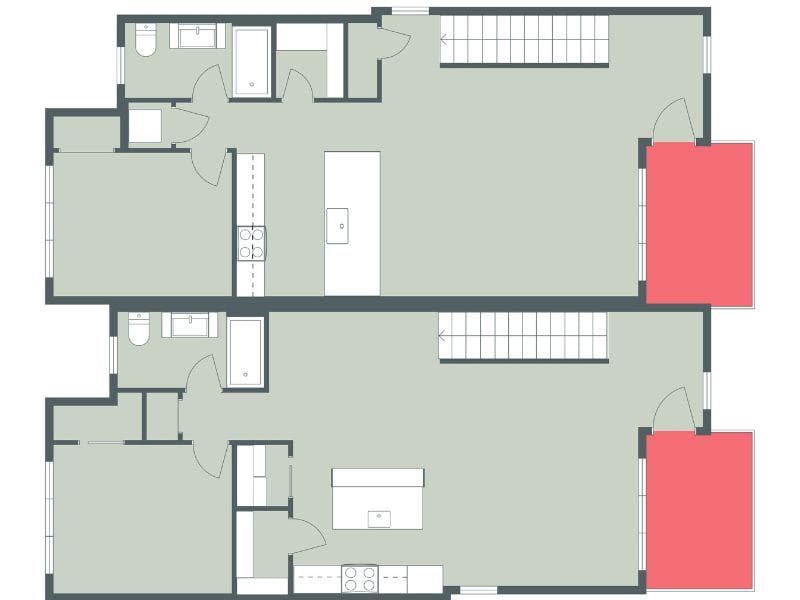
What Is Gross Building Area?
Gross Building Area (GBA) is generally defined as the total building area, including the outside walls. GBA includes all floors, interior and exterior walls, staircases, and other structural elements. There are a few exclusions, which we will cover in more detail later. For example, features extending from a building’s exterior, such as open decks, balconies, and fire escapes. GBA is one of several measurements that can be important for construction estimates, building permits, property loans, revenue estimates, and more.
Note that definitions of GBA, including which areas count towards it, vary depending on the measurement standard and location. Hence, it's advisable to check with local authorities or a professional appraiser for the prevalent standards in your area. Many countries are moving towards International Property Measurement Standards (IPMS), developed by more than 80 professionals and non-profit organizations, to document international property measurement standards.
In some locales, the Gross Building Area (GBA) is referred to as the Gross Construction Area or the Gross External Area. The International Property Measurement Standards (IPMS) refer to this measurement as IPMS 1.
How to Calculate Gross Building Area
Gross Building Area is essentially the total area of all the floors of a building, measured to the outside of the external walls. Here are a couple of ways to calculate GBA:
Option 1: Use an existing blueprint or floor plan
If you have an existing blueprint or floor plan for the building, you can import it into floor plan software like RoomSketcher. With RoomSketcher’s built-in area calculator, you can get your Gross Building Area result in seconds - just click to exclude any uncovered external balconies or decks on the floor plan and then choose the “Gross Floor Area” calculation. See Calculate the Total Area of a Floor Plan for more information on RoomSketcher’s area calculations.
Option 2: Measure onsite
You can also measure up the property if you don’t have access to an existing floor plan.
- Start with a walkaround - Walk around the property to get an idea of the shape.
- Sketch the property on paper or tablet - Make a sketch of the property on paper or create a digital sketch using floor plan software on your tablet.
- Find the rectangles - Now work on each floor. Note whether each floor is a simple rectangle or break it down into smaller rectangles (so you can multiply length x width for each rectangle and add them together).
- Get the measurements - Measure each rectangle using a tape measure, roto wheel, or a laser to determine the size of each rectangle, factoring in internal and external wall widths.
- Do the math - Multiply the length and width of each rectangle to calculate its size. Add together all the rectangular areas on the floor. Repeat for all floors, and sum the result to calculate the building’s total GBA.
Top RoomSketcher Tip
IPMS standards recommend reporting each floor individually, along with the total GBA for the building.
What is Included in Gross Building Area?
Gross Building Area generally includes everything inside a building. However, since all buildings are different, it’s not quite that simple. For example, what about balconies that extend from the structure? Or rooftop terraces? How about external stairs? Examples of areas that are generally included in the GBA:
- Atriums and lobbies (but only count the floor level in the calculation - do not count the open areas above).
- The footprints of stairways, elevator/lift shafts, and vertical duct shafts are counted on each floor through which they pass.
- Covered outer balconies and walkways are included if used for an occupant's operational functions. Count the area only to the drip line (an imaginary line extending down from the edge of a roof, balcony, or walkway immediately above.)
- Rooftop terraces and parking spaces, even if the specific area is not roofed.
- Basements that are usable for building occupants and have reasonable access.
- Unheated and uncooled areas of industrial buildings, since occupants may use them.
- External stairs that lead to upper levels (except open framework fire escapes, which are excluded.)
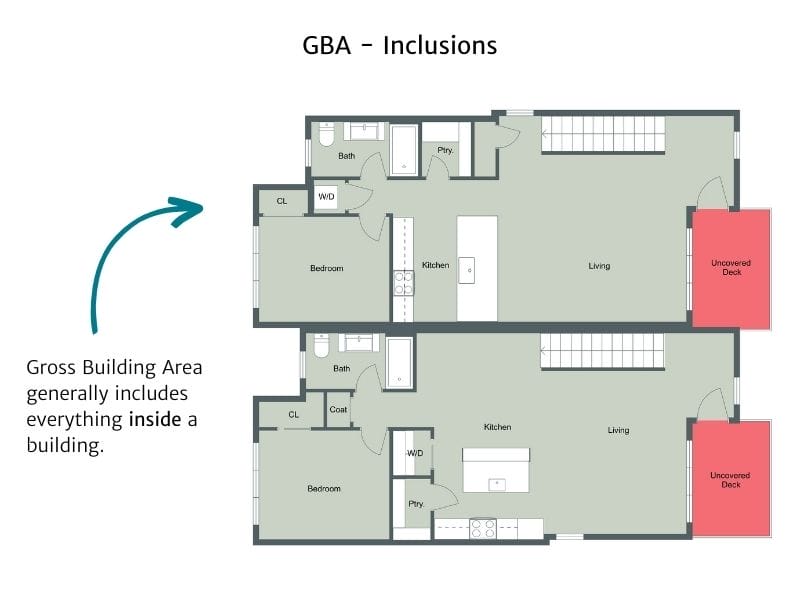
Top RoomSketcher Tip
Because standards vary slightly worldwide, check with your local authorities for a complete list of the standard inclusions in your area.
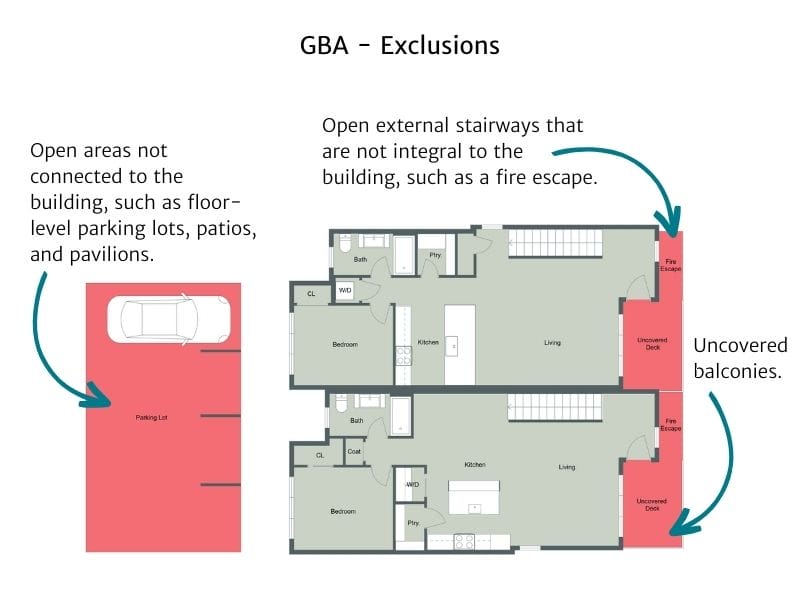
What Do You Exclude from GBA?
The following are examples of areas to exclude from GBA measurements:
- Open areas not connected to the building, such as floor-level parking lots, patios, and pavilions.
- Uncovered balconies.
- Open areas on upper floors (above a lobby or atrium).
- Open light wells.
- Areas with less than a 3-foot ceiling height.
- Basements, if they lack reasonable access and usability.
- Open external stairways that are not integral to the building, such as a fire escape.
- Exterior Loading Docks.
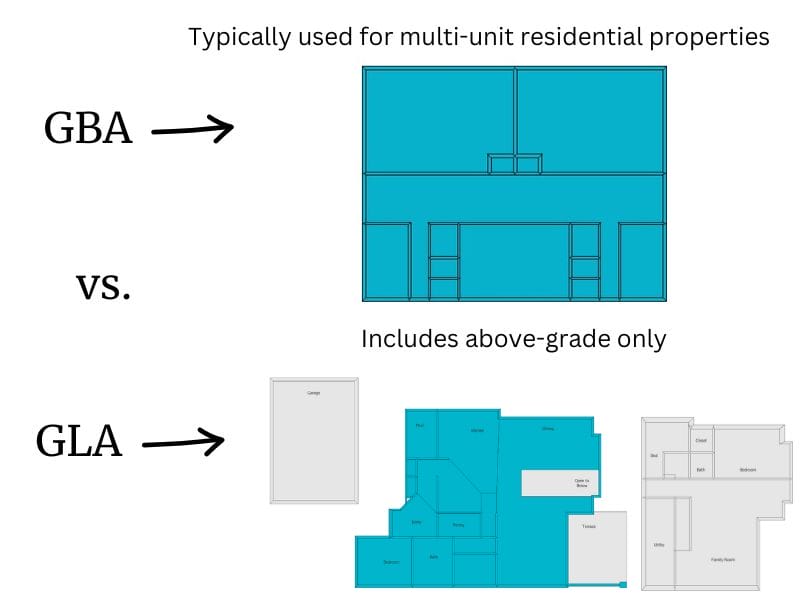
Comparing GBA With Other Measurement Standards
Appraisers and other real estate professionals measure commercial and residential buildings. In doing so, they may calculate Gross Living Area (GLA), Total Living Area (TLA), and Gross Internal Area (GIA), among others, to prepare their clients' reports.
Each measurement is different in some way and serves another purpose.
Gross Building Area (GBA) vs. Gross Living Area (GLA)
GBA measures an entire building, while GLA focuses on living space that is permitted, finished, and above ground.
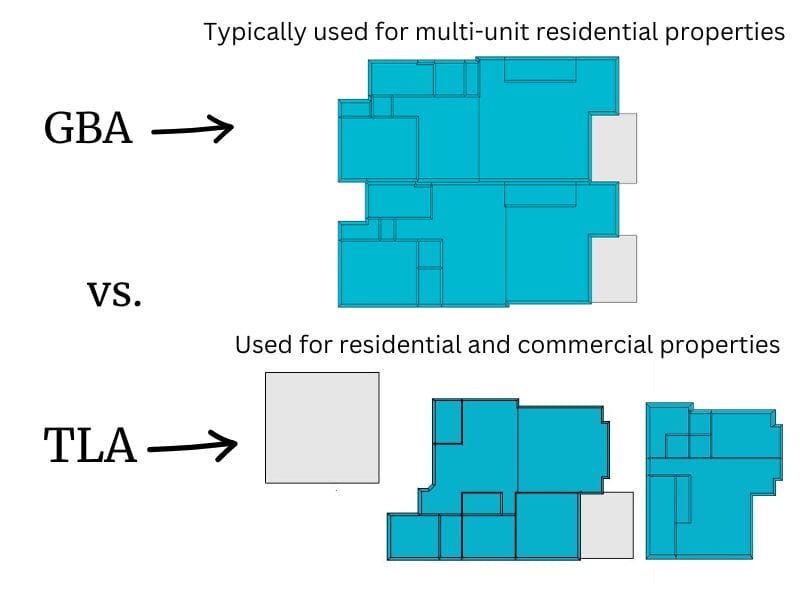
Gross Building Area (GBA) vs. Total Living Area (TLA)
Total Living Area (TLA) includes above and below-grade finished space and may also include detached living areas if permitted and finished - but the focus is living space. GBA measures the entire building area, including areas unsuitable for living in, such as atriums, mechanical rooms, and elevator shafts in commercial buildings or shared interior stairways in multi-family residential buildings.
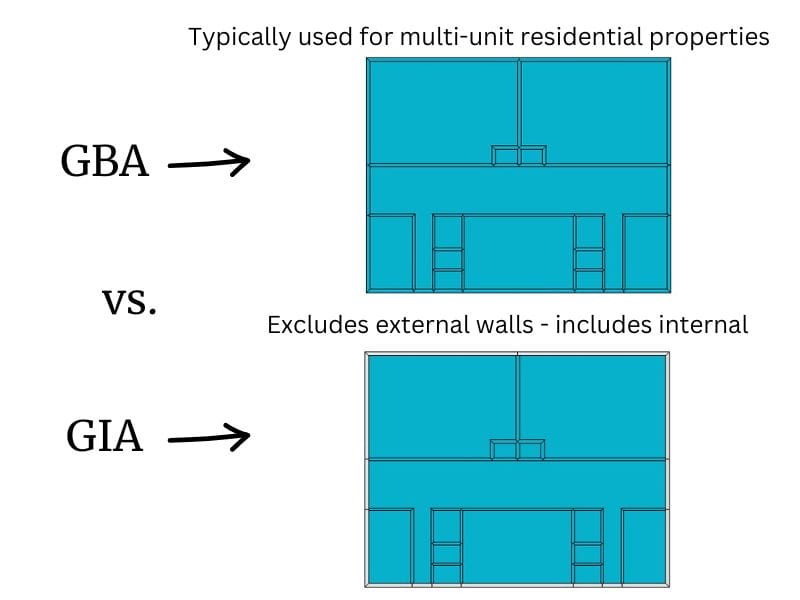
Gross Building Area (GBA) vs Gross Internal Area (GIA)
GIA includes everything within the internal faces of exterior walls, while GBA includes external walls.
FAQs about GBA Measurement
Yes, if the basement is functional with a reasonable way to access it; otherwise, it is generally excluded.
Generally, inner and outer balconies are included if occupant-operated and covered. Exterior balconies are measured to the drip line.
Gross Floor Area (GFA) is the total fully enclosed floor area, excluding areas like outside balconies not surrounded by an external wall, whereas GBA includes covered exterior balconies used for occupant purposes.
Make your GBA Measurement and Reporting Easier
Gross Building Area is one of several important metrics in multi-family properties and commercial real estate. You can calculate a building's GBA by measuring up each floor or by using floor plan software, like RoomSketcher, to improve the process. Even more, RoomSketcher allows you to turn your hand-drawn sketches into professional floor plans.
If you want to discuss our services or ask questions about Gross Building Area calculations, please contact us; we would love to help you.
Don't forget to share this post!
Recommended Reads
What is Gross Living Area (GLA) and How Do You Calculate It?
Learn what Gross Living Area (GLA) means, why it's important, and how to accurately calculate it for a property. Discover our expert guide.
How to Measure Floor Area and Calculate Square Footage
Measure floor areas easily, quickly, and accurately. The correct results are essential for ordering materials for renovation projects, preparing sales and marketing materials for a property, and designing the furniture layout.
Designing an Efficient Floor Plan: 11 Key Characteristics to Create Your Perfect Space
Create an efficient floor plan that balances functionality, flow, and aesthetics with the help of these 11 key characteristics.
